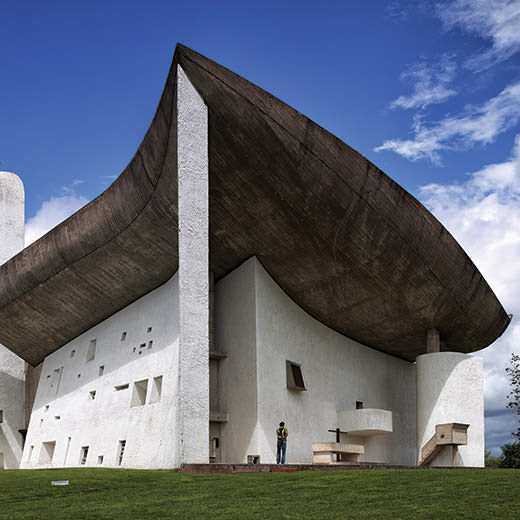
Architecture, is not like any other art or discipline, as it can be experienced as a whole. Unlike painting, cinema or music, architecture plays with form, space, placement, materials and function; making it really difficult to get the whole experience if not visiting it.
Place
When architects project a house, they must take into account the locaction it will be built in, regarding this topic, buildings can establish different relationships with its environment.
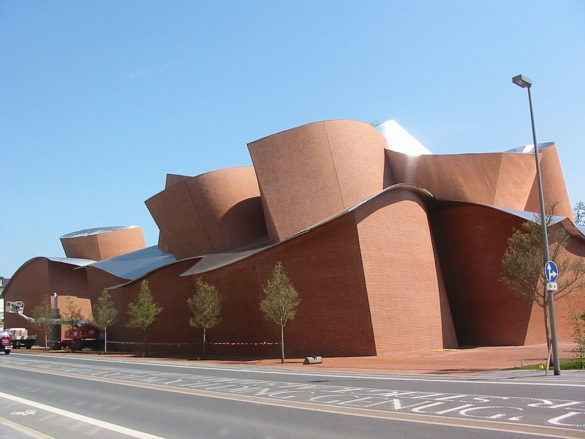
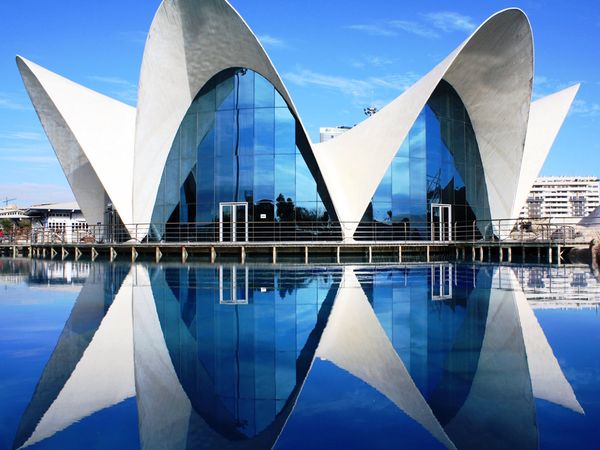
Of contrast
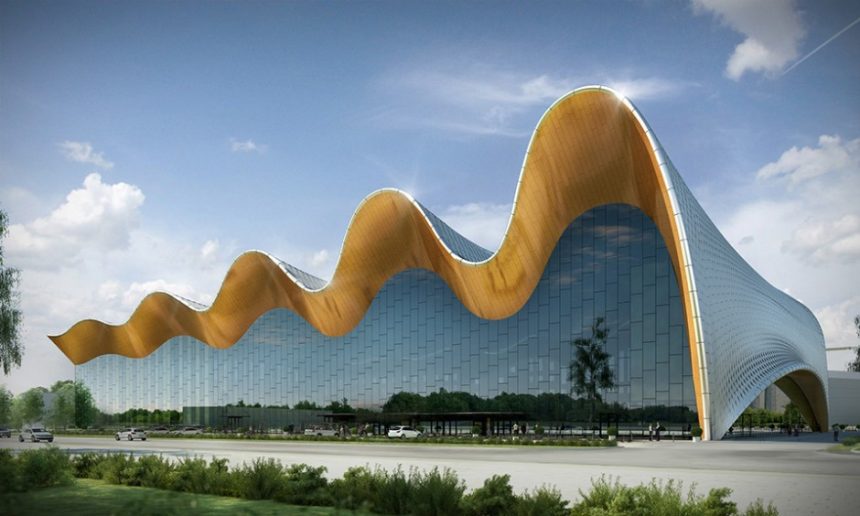
In this type o relationships, the buildings are either juxstaposed (they clearly dominate the landscape, considerably changing it), or allien to it (they do not fit into the landscape, making it stand out).
some examples of this type of relationship are:
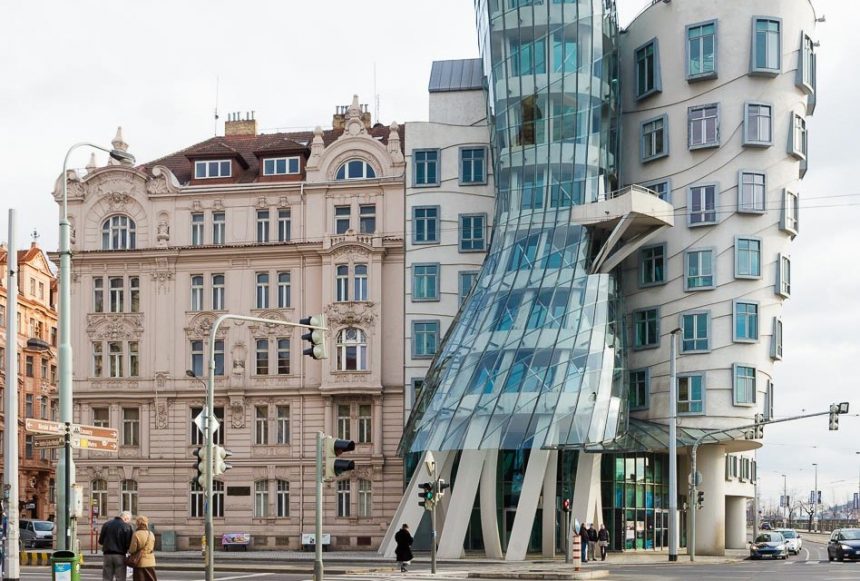

Frank Ghery’s Dancing House 
Santiago Calatrava’s «Centollo»
Of camouflage
the buildings melts with its surroundings via memesis (imitation of the place)
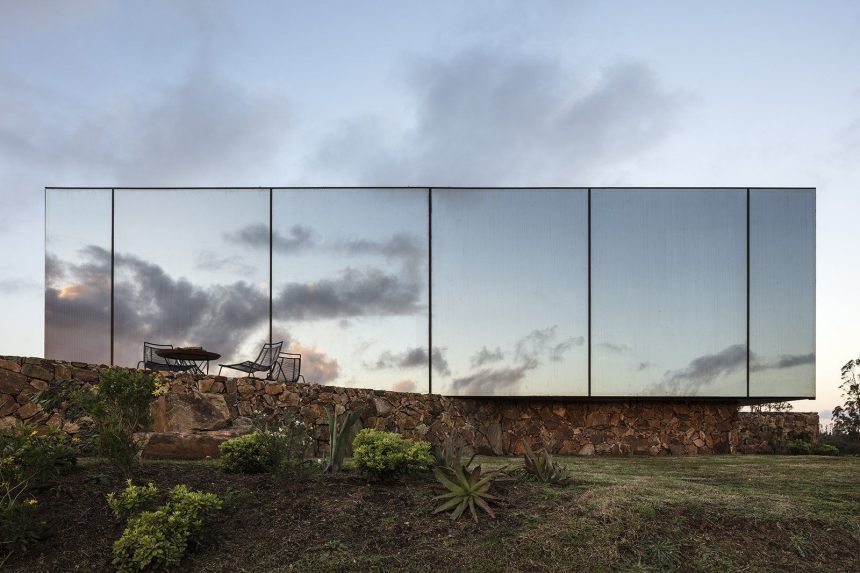




Villa Valls, SeARCH, CMA 
VIlla Valls, SeARCH, CMA
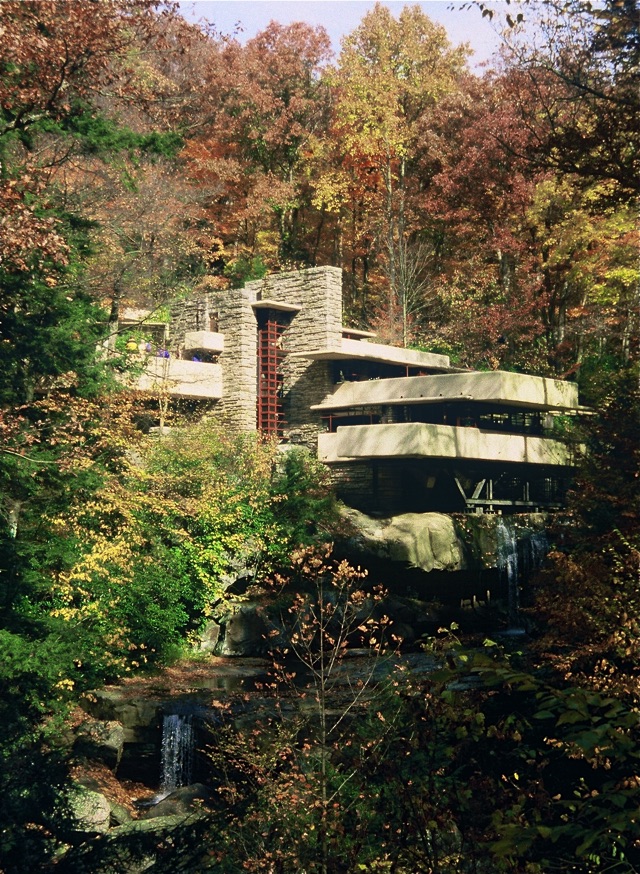
Of organicisim
unlike camouflge, when an organicism realtionship is stablished, the elemets of the landscape are reinterpreted to form a building that doesn’t camouflage with the place, but it’s also not allien to it. The building and the landscape work in a synergy and perfect harmony. Frank LLoyd Wright and Alvar Aalto used this concept on their buildings, for example:
Of contextualism
The relationship with its surroundings is justifiable
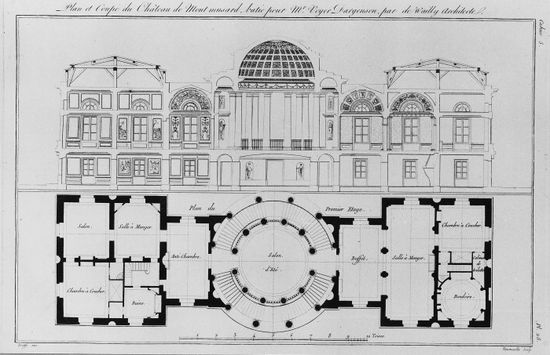
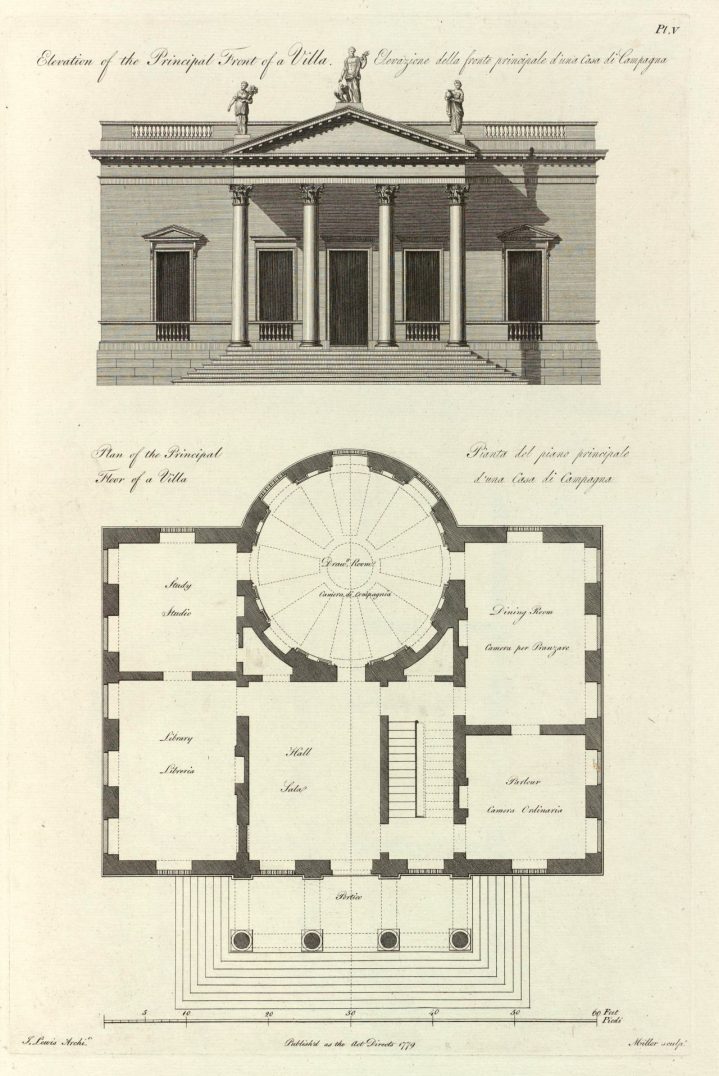
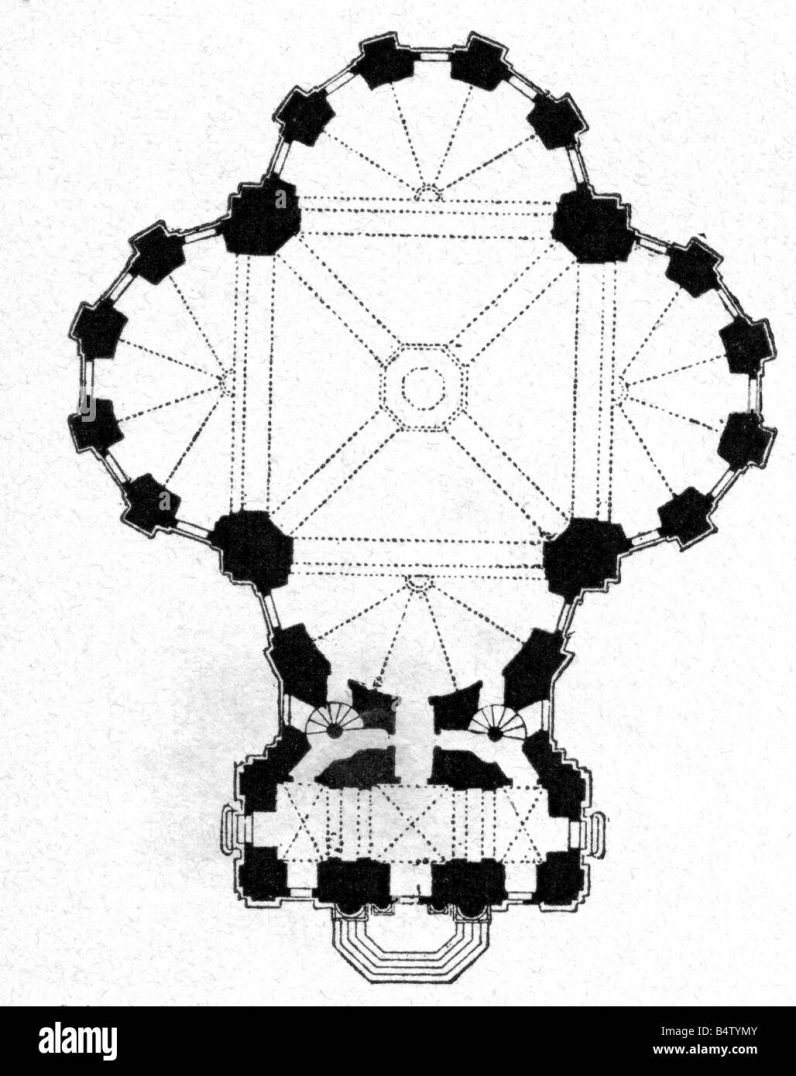
Space
classic space
- compact and closed becaouse of thick loadbearing walls
- Renaissance: at least one axis of symmetry, centralized
- Barroque: centralized, two axis of symmetry
spaces without a centre
- Japanese, based on modular tatamis.
- sum of individual rooms
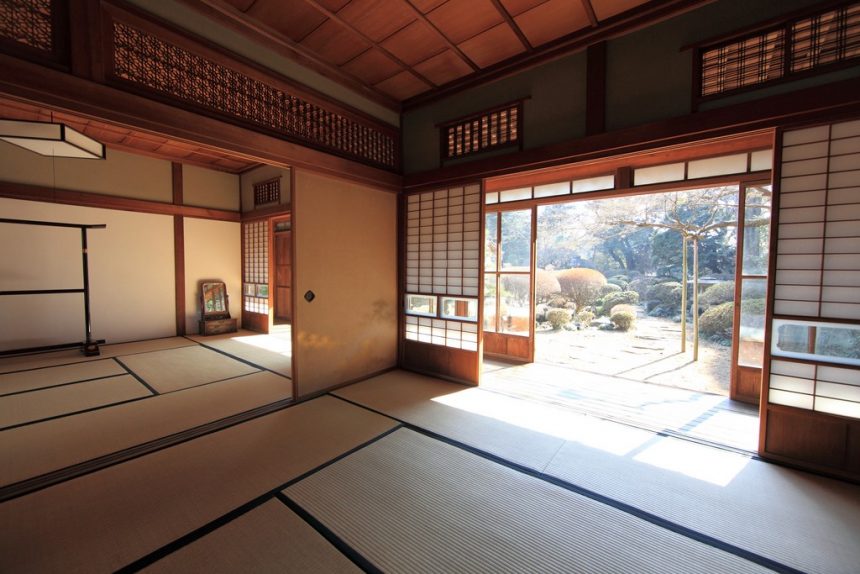

Modern space
- breaks the «box». Connections, double heights, free floor plans.
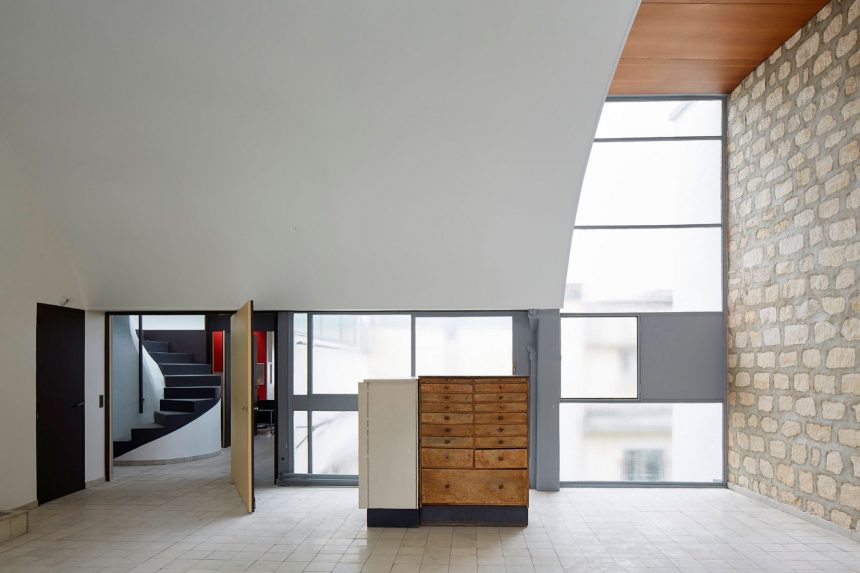

Contemporary space
- entire space of the building is continuous and unique.
- confusion
- free section, end of the horizontality
Form
Rythm
- repetition of forms in the space
Axis
- linear element around which the elements are equally distributed
Symmetry
regular arrangements around an axis or point
Hierarchy
supremacy of an elemet over the others
Module
unitary elemet that serves as a proportional unit
Grid
conposition based on a grid or axes
Movement
irregularity inspires movement
Unity
the elemets seem like they belong to a whole
centrality
organization around a centre that drives attention towards it
Balancing
not meaning symmetry, but just a global sense of equilibrium in the building, staticism.
Limits
Where a space ends in order for another one to start, would it be interior-exterior, functional differences…
Light
Without light there is no space, Light gives shape to the space as well as the space gives form to the light.
Contrast
contrast in material, form, scale…
colour
highlight certain parts of a building, expression, for children…
Texture
surface of the elements
Proportion
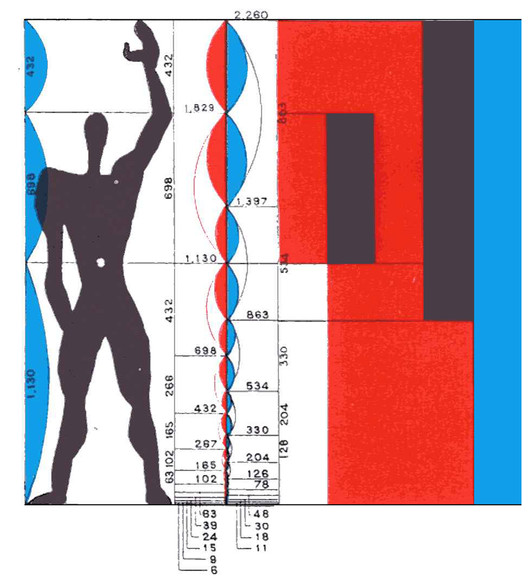
not always in a classical way, proportion is also used in modern architecture (Le Corbusier and the golden ratio)
Scale
if we change the natural scale of a building (relationship human-building), it will have an expressive effect. We are used to human scales, and when we change it, we notice. For example San Pietro del vaticano.
Function
we can divide function in three conceptions of funcionalism
Mechanical Funcionalism
Started in the industrial revolution. Form is a direct consequence of function, without taking esteticism into account.
Sullivan daid «form follows function»
Form is not the objective, but the result of the work.
Organic Funcionalism
Adapts to the function it must be used for, adapted to human needs, social activities, environmet…
It developes from inside outwars
Moralistic Funcionalism
the form is trying to transmit intentionally what is the function of the building. The form is always linked to the function.
Materiality and Structure
can be realated to VItruviu’s Firmitas
Form is related o materials, that are both connected to technology.
Use the materials according to properties and qualities.
Materials and technologies are constantlly replaced by new ones, but the ideas and concepts of the buildings and primitive constructions survive through history.
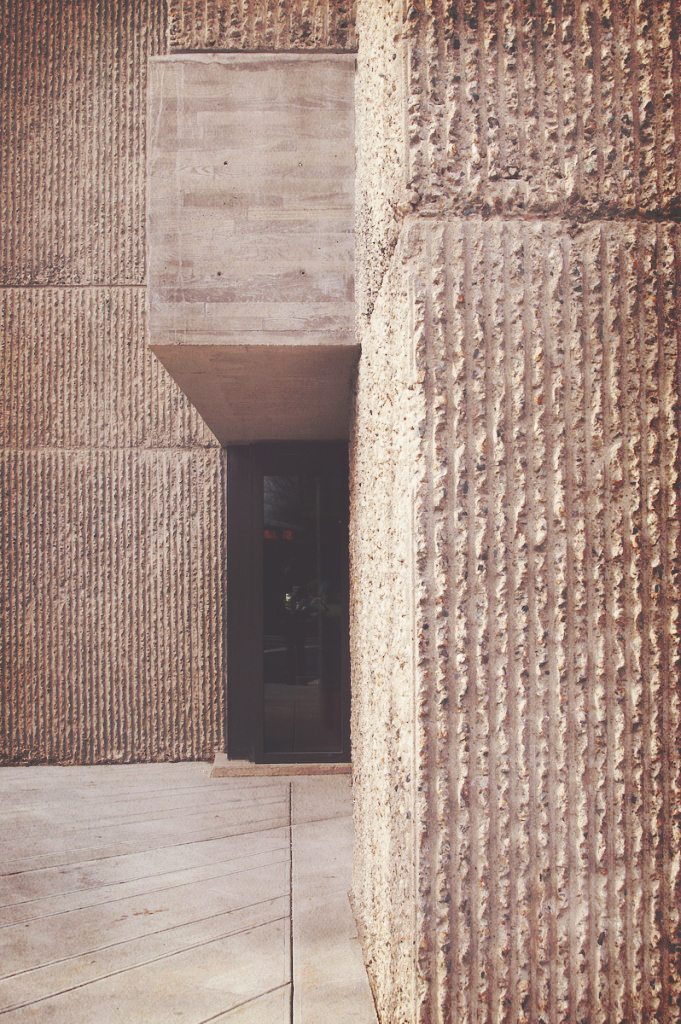
Stone
traditional material, heavy, sturdy, still used nowadays. Structural function of stone has been replaced with reinforced concrete (lighter and sturdier).
Today it is mainly used with decorative intentions.
Earth
poor material, non resistant.
Adobe: blocks of earth reinforced with straws to avoid retracting. Sundried
Shutterings: Rammed earth walls, compacted, can be enriched
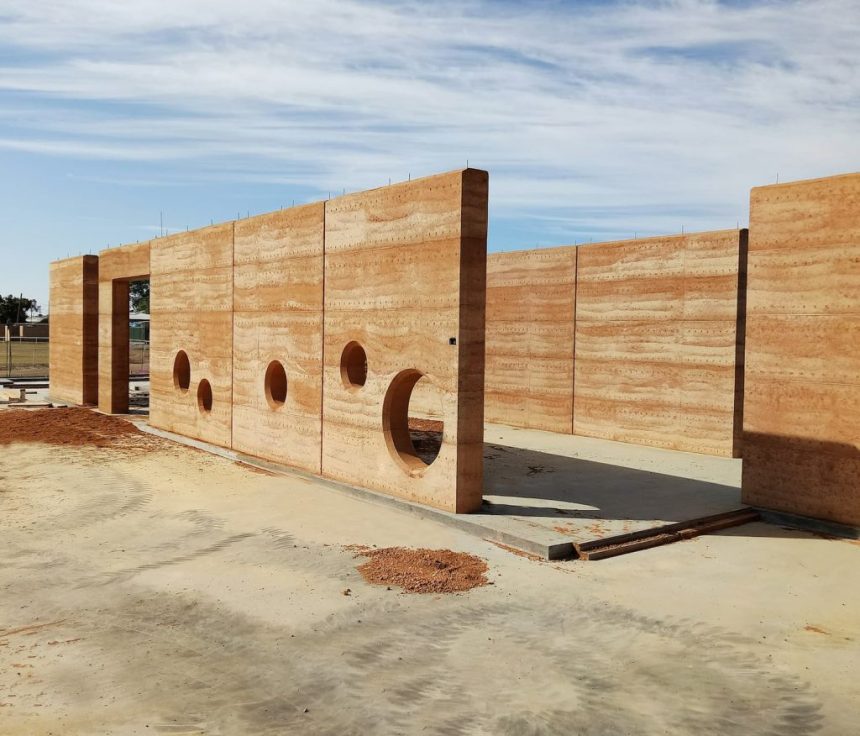

Rammed earth wall 
Stone contemporary wall
all this kinds of traditional materials are sustainable, so, who knows if future architecture will be made form them?
Bricks
cooked clay.
there are infinite possibilities thaks to reinforcements
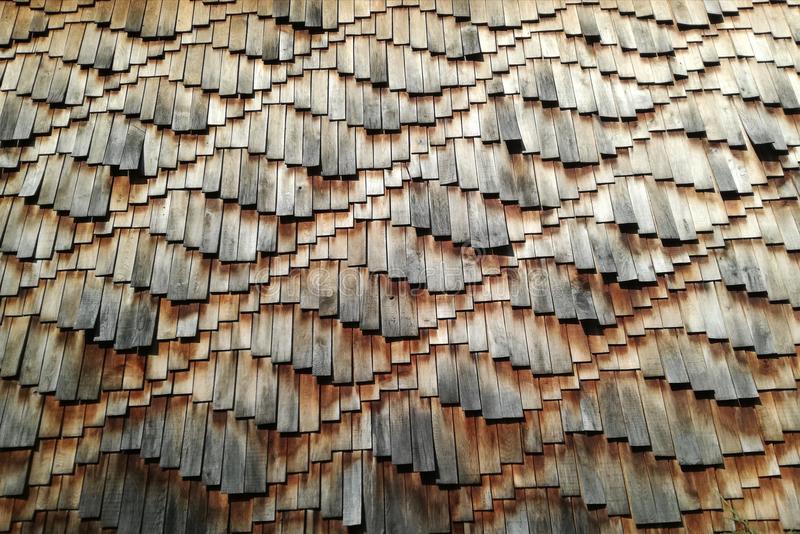
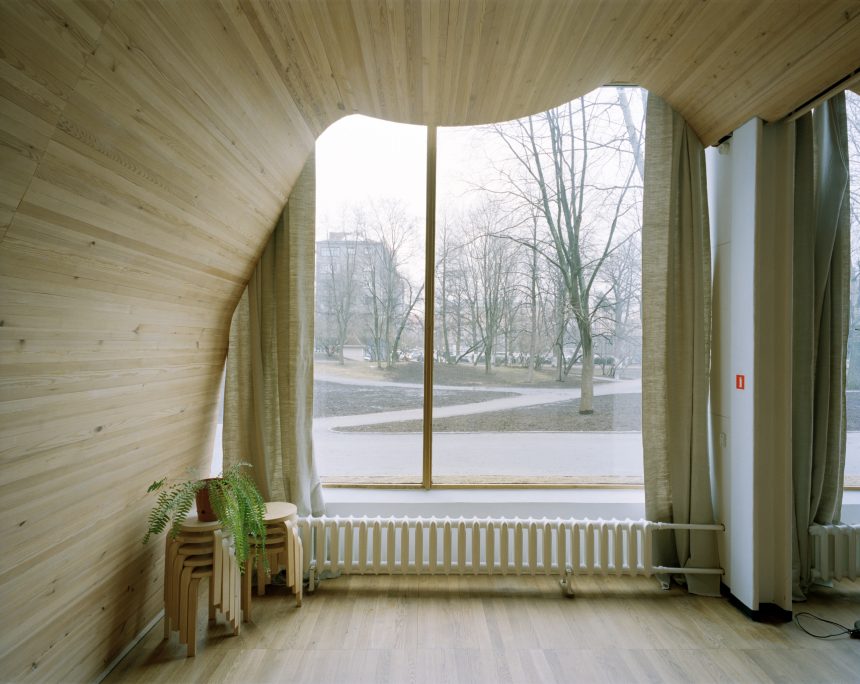
wood
can be used in very simple structures or in more elaborated constructions.
Its possibilities are not limited to traditional uses.

ReN_008232_1 001 

Irkutsk, Russia – August 24, 2016: Old wooden houses in Irkutsk. Wooden architecture of Russia
Steel
relatively new material (industrial revolution)
First decades of the 20 century, ot was widely spread.
concrete
can be built in situ or precasted
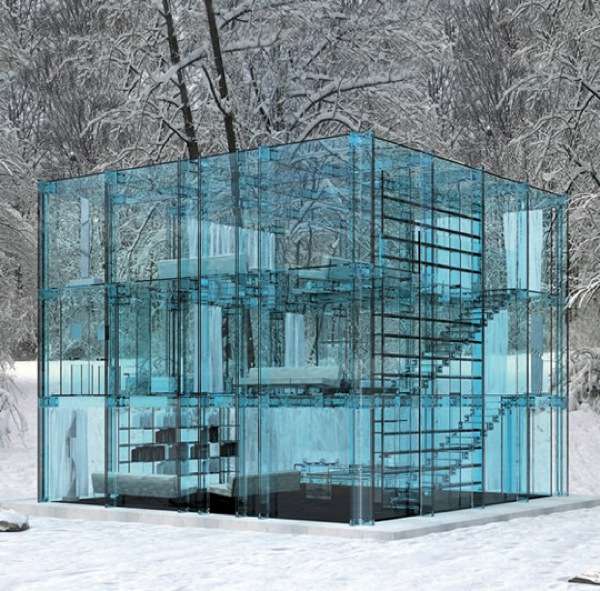
glass
allow light to come in being able to close the structure.
it gives lightness to the building.
Technology
the way the materials and technics are implemented.
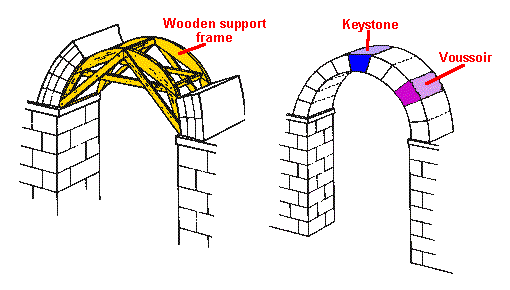
roman constructions 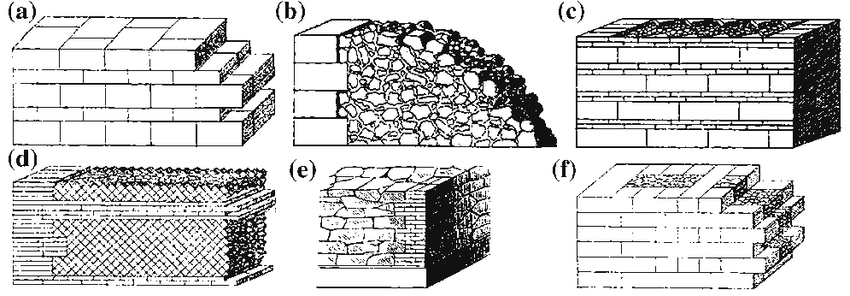
roman 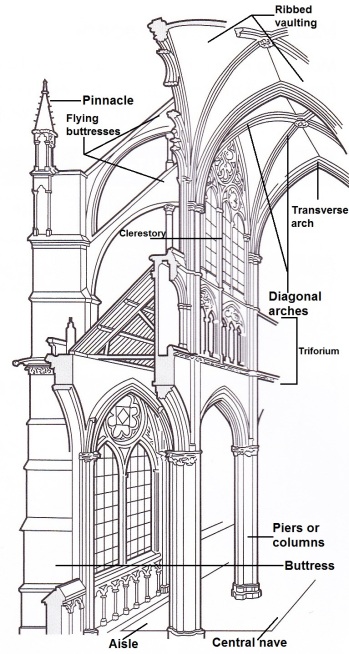
gothic system 
cad 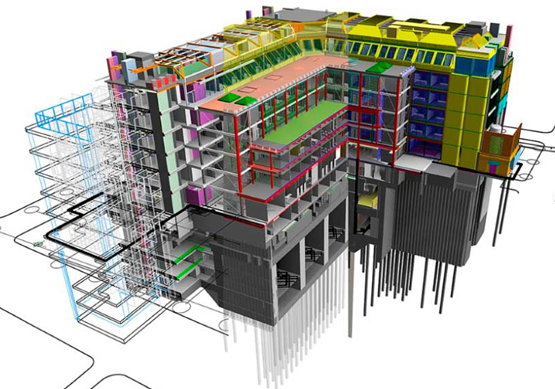
bim